 Overview
OverviewThere are two types of Hammertoes, Flexible hammertoes. If the toe still can be moved at the joint, it's a flexible hammertoe. That's good, because this is an earlier, milder form of the problem. There may be several treatment options. Rigid hammertoes. If the tendons in the toe become rigid, they press the joint out of alignment. At this stage, the toe can't be moved. It usually means that surgery is needed.
Causes
The main cause of hammer toe is poorly fitted and/or poorly designed footwear. Any footwear that is too tight in the toe box, especially high-heeled shoes, can push the toes forward, crowding one or more of them into a space that is not large enough to allow the toes to lie flat and spread as they should. Other causes include the following. Changes in foot anatomy. Sometimes the metatarsal bones in the ball of the foot can ?drop,? creating a situation in which the toes do not make contact with the surface of the shoe. The toes may then contract at one or both of the joints to re-establish contact with the surface. Traumatic injuries in which toes are jammed or broken. Diabetic neuropathy. This can cause abnormal foot biomechanics due to nerve and/or muscle damage. Damage to nerves and muscles from other conditions, such as arthritis or stroke. Heredity.

Symptoms
A toe stuck in an upside-down "V" is probably a hammertoe. Some symptoms are, pain at the top of the bent toe when putting on a shoe. Corns forming on the top of the toe joint. The toe joint swelling and taking on an angry red colour. Difficulty in moving the toe joint and pain when you try to so. Pain on the ball of the foot under the bent toe. Seek medical advice if your feet regularly hurt, you should see a doctor or podiatrist. If you have a hammertoe, you probably need medical attention. Ask your doctor for a referral to a podiatrist or foot surgeon. Act now, before the problem gets worse.
Diagnosis
Your doctor is very likely to be able to diagnose your hammertoe simply by examining your foot. Even before that, he or she will probably ask about your family and personal medical history and evaluate your gait as you walk and the types of shoes you wear. You'll be asked about your symptoms, when they started and when they occur. You may also be asked to flex your toe so that your doctor can get an idea of your range of motion. He or she may order x-rays in order to better define your deformity.
Non Surgical Treatment
Apply a commercial, nonmedicated hammertoe pad around the bony prominence of the hammertoe. This will decrease pressure on the area. Wear a shoe with a deep toe box. If the hammertoe becomes inflamed and painful, apply ice packs several times a day to reduce swelling. Avoid heels more than two inches tall. A loose-fitting pair of shoes can also help protect the foot while reducing pressure on the affected toe, making walking a little easier until a visit to your podiatrist can be arranged. It is important to remember that, while this treatment will make the hammertoe feel better, it does not cure the condition. A trip to the podiatric physician?s office will be necessary to repair the toe to allow for normal foot function. Avoid wearing shoes that are too tight or narrow. Children should have their shoes properly fitted on a regular basis, as their feet can often outgrow their shoes rapidly. See your podiatric physician if pain persists.
Surgical Treatment
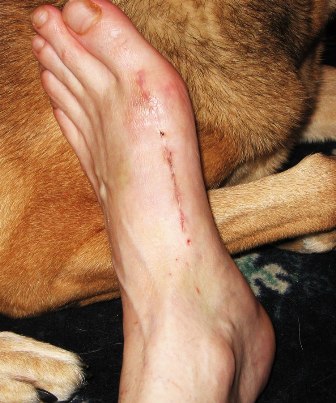
If your hammer, claw, or mallet toe gets worse, or if nonsurgical treatment does not help your pain, you may think about surgery. The type of surgery you choose depends on how severe your condition is and whether the toe joint is fixed (has no movement) or flexible (has some movement). A fixed toe joint often requires surgery to be straightened. A flexible toe joint can sometimes be straightened without surgery. Surgery choices include Phalangeal head resection (arthroplasty), in which the surgeon removes part of the toe bone. Joint fusion (arthrodesis), in which the surgeon removes part of the joint, letting the toe bones grow together (fuse). Cutting supporting tissue or moving tendons in the toe joint. How well surgery works depends on what type of surgery you have, how experienced your surgeon is, and how badly your toes are affected.
 A bunion is the enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs as a result of the misalignment of the bones of the big toe. This leads to stretching of the ligaments and tendons around the big toe joint and causes soft tissue over the joint to become inflamed and painful. There may be additional bone formation (exostosis) in the joint and the skin around the joint may become red and tender. Over time the cartilage in the joint can break down, leading to arthritis.
A bunion is the enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs as a result of the misalignment of the bones of the big toe. This leads to stretching of the ligaments and tendons around the big toe joint and causes soft tissue over the joint to become inflamed and painful. There may be additional bone formation (exostosis) in the joint and the skin around the joint may become red and tender. Over time the cartilage in the joint can break down, leading to arthritis.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
